Git is quickly becoming one of the world's most popular solutions for version control. Many popular projects are only available through Git hosts, and many teams are beginning to appreciate the value of the distributed nature of Git. By default, Git uses whatever you’ve set as your default text editor via one of the shell environment variables VISUAL or EDITOR, or else falls back to the vi editor to create and edit your commit and tag messages.
Vim - the text editor - for Mac OS X. Contribute to macvim-dev/macvim development by creating an account on GitHub.
Version Control is a “must” even for simple projects. That’s why in the next posts I am going to discuss how to integrate Visual Studio Code with Git and use github and Visual Studio Online as a remote provider for Git.
It is possible to reconfigure the text editor for Git whenever you want to change it. Note that Vim is the default editor for many programs. When you previously used git commit for committing the first hello.html version to the repository, you included the -m flag that gives a comment on the command line. The commit command allows interactively editing comments for the commit. Any Mac text editor can be configured to work with Git commits. As a fan of both command line and simple/efficient text editors, I've found both MacVim and TextMate to be the best. If you aren't comfortable with command line type things, or with vi, I would recommend TextMate. It's an extremely nice.
Visual Studio Code supports local and remote Git repositories but right now we will discuss local Git repositories only. And first of all we need to install Git on our Mac (if you still don’t have it).
I know at least two ways to install Git: using the following link or from Terminal window. If you decide to install Git directly from git-scm.com, you need to simply download the package and run the pkg file from there. But if you don’t change security settings, probably you will get the following window:
In order to fix the problem you should open System Preferences -> Security & Privacy and allow to run the package. You should not change any parameters there because Mac OS will notify you about the latest blocked package and you can simply click Open Anyway button there:
The second way allows using Terminal window to install Xcode command line developer tools. Simply open the Terminal from Visual Studio Code by activating context menu there for any file and calling Open in Console menu item.
In the Terminal type Git and click Enter. You will get the message that Xcode tools are not installed and suggestion to install them. In this case you will not have any problems with security. Git tools will be installed directly from Apple. It’s not always the latest version of Git but it will successfully work with Code.
Pay special attention that once you install Git you need to restart Visual Studio Code.
Once Git is installed and Code is restarted you will be able to activate Git for current workspace (folder) by clicking Initialize Git repository in GIT view.
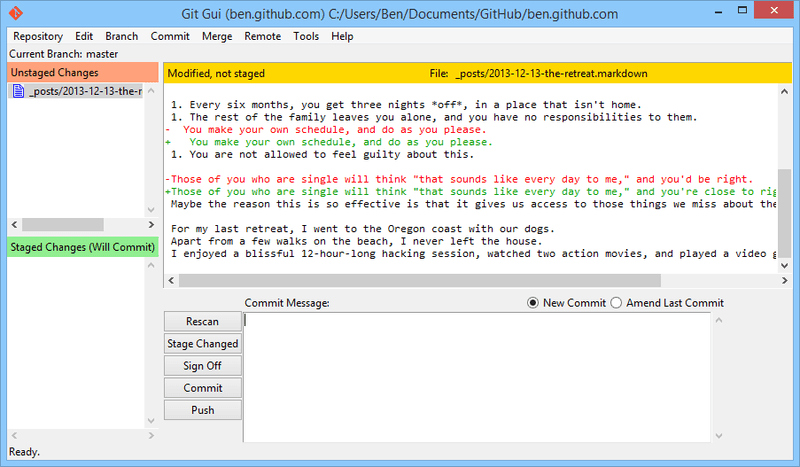
And that’s all. Now you can work with Git locally. Using GIT view you can see what files are changed. After clicking them you can review the current and the previous versions of the file:
Code editor is smart enough to highlight all changes.
Working with files locally you have access to the standard commands. By clicking any file and activating the context menu you can put the file on stage:
And using the menu at the top of the GIT view you can commit changes or get access to Git output:
Finally, clicking the branch name in the status bar you can open command line for git tool.
Using the command line you can execute only two commands: git checkout and git brach.
Both commands have only one parameter, that is the name of a branch. The first command allows to checkout files to a new or an existing branch and the second one allows to switch Code to an already existing or a new branch.
That’s all for today. In the next topic we will discuss how to use Visual Studio Online as a remote repository for Git.
I would prefer to write my commit messages in Vim, but it is opening them in Emacs.
How do I configure Git to always use Vim? Note that I want to do this globally, not just for a single project.
Mark Amery20 Answers
If you want to set the editor only for Git, do either (you don’t need both):
- Set
core.editorin your Git config:git config --global core.editor 'vim' - Set the
GIT_EDITORenvironment variable:export GIT_EDITOR=vim
If you want to set the editor for Git and also other programs, set the standardized VISUAL and EDITOR environment variables*:
* Setting both is not necessarily needed, but some programs may not use the more-correct VISUAL. See VISUAL vs. EDITOR.
For Sublime Text:Add this to the .gitconfig. The --wait is important. (it allows to type text in sublime and will wait for save/close event.
'subl' can be replaced by the full path of the executable but is usually available when correctly installed.
Ry-♦Copy paste this:
In case you'd like to know what you're doing. From man git-commit:
ENVIRONMENT AND CONFIGURATION VARIABLES
The editor used to edit the commit log message will be chosen from the GIT_EDITOR environment variable, the core.editor configuration variable, the VISUAL environment variable, or the EDITOR environment variable (in that order).
On Ubuntu and also Debian (thanks @MichielB) changing the default editor is also possible by running:
Which will prompt the following:
Koen.Koen.In windows 7, while adding the 'Sublime' editor it was still giving me an error:
Aborting commit due to empty commit message.
Sublime was not able to keep the focus.
To fix this I opened the .gitconfig file in c:/users/username/ folder and added the following line with --wait option outside the double quotes.
Hope its helpful to somebody facing similar issue with Sublime.
Rubens MariuzzoIn Windows 7, setting editor to Notepad++
- Open any text editor.
- Open this file:
C:UsersYOUR_USERNAME.gitconfig - Add this section to the bottom:
- Save and close the file.
- When you're committing with git, just write
git commitand pressEnter. It will pop open Notepad++. - Write your commit message at the top of the file, and save and close the file. Done!
To Make Visual Studio Code (vscode) your default git editor
 Marcelo MasonMarcelo Mason
Marcelo MasonMarcelo MasonAnd if you are working with designers using the command line then Pico, and dont know short cuts ;)
Or
tristanbaileytristanbailey
Html Editor For Mac
Atom needs to be configured to run from the command line for the above to work:
OS X: install shell commands from Atom: menu bar > Atom > Install Shell Commands
Windows: no action required - atom is configured to run from the command line by default
2Toad2ToadHit Ctrl+S to save your commit message. To discard, just close the notepad window without saving.
In case you hit the shortcut for save, then decide to abort, go to File->Save as, and in the dialog that opens, change 'Save as type' to 'All files (*.*)'. You will see a file named 'COMMIT_EDITMSG'. Delete it, and close notepad window.
Edit: Alternatively, and more easily, delete all the contents from the open notepad window and hit save. (thanks mwfearnley for the comment!)
I think for small write-ups such as commit messages notepad serves best, because it is simple, is there with windows, opens up in no time. Even your sublime may take a second or two to get fired up when you have a load of plugins and stuff.
SнаđошƒаӽSнаđошƒаӽThis provides an answer for people who arrive at this Question that may want to link an editor other than vim.
The linked resource, by Github,is likely to be kept up to date, when editors are updated, even if answers on SO (including this one) are not.
Github's post shows exactly what to type in to your command line for various editors, including the options/flags specific to each editor for it to work best with git.
Notepad++:git config --global core.editor 'C:/Program Files (x86)/Notepad++/notepad++.exe' -multiInst -notabbar -nosession -noPlugin'
Sublime Text:git config --global core.editor 'c:/Program Files/sublime text 3/subl.exe' -w'
Atom:git config --global core.editor 'atom --wait'
The commands above assume your editor has been installed in the default directory for a windows machine.
The commands basically add the text between double-quotes to .gitconfig in your home directory.
On a windows machine home is likely to be C:Usersyour-user-name, where your-user-name is your login name.
From the command line, you can reach this directory by typing in cd ~.
for example, a command above would be add the following line under the [core] section like so:[core] editor = 'C:/Program Files/sublime text 3/subl.exe' -w
If you have a different editor, just replace with the path to your editor, using either method above. (and hope no flags are needed for optimal usage.)
SherylHohmanSherylHohmanTo follow these instructions in Windows make sure you have installed git for Windows. In Windows, I like to use Git BASH so that it feels more like Linux.
First, we want to create a special Sublime Text project so that we can specify special project settings we want set whenever git calls the editor, to make things easier when editing in git. For example, I normally set my ruler to 120 chars in most projects, but for git commit messages I want it to be 72 chars so that it fits nicely in a terminal when you call git log or git lg.
1. Create a Sublime Text project with settings we want to use to edit git commit messages
Open Sublime Text and go to 'File' --> 'New Window' to create a new anonymous project. Go to 'Project' --> 'Save Project As...' and choose a place to save it. In Linux I saved it in my Linux home directory with the file name .gitconfig.sublime-project. It's path is therefore: ~/.gitconfig.sublime-project. In Windows also save it in your home directory, ex: C:UsersMY_USER_NAME.gitconfig.sublime-project Now go to 'Project' --> 'Edit Project' to edit the project settings. Paste the following and save the settings. Make any further edits for your project settings if desired.
2. Set the editor to be used by git
Now we need to set the editor to be used by git, by editing the .gitconfig file.
For Linux:
Your user copy of this will be located in ~/.gitconfig. Open this file and add the following lines. Be sure to use the proper path name to the git project you just created above! I'm using ~/.gitconfig.sublime-project.
The --wait is important, as it forces git to wait until you close the file before it continues on. The --project line is important to tell Sublime Text which project you want opened whenever git opens Sublime.
Per @digitaldreamer's answer above (https://stackoverflow.com/a/2596835/4561887), 'subl can be replaced by the full path of the executable but [the alias subl] is usually available when [Sublime is] correctly installed.'
For Windows:
For Windows, first read the Linux instructions for background info. Now we will do something almost identical.
(OPTIONAL: create a subl alias for use in Git BASH):
Open up a text editor (ex: Notepad, Notepad++, Sublime Text, Geany, etc), and create a file called '.bash_profile' in your home directory. Its path will therefore be: C:UsersMY_USER_NAME.bash_profile. Save the following into it:
This creates a Git BASH alias called subl that we can now use in Git BASH for Windows, to easily open Sublime. This step isn't required but it's useful for general Git BASH use. Now you can call subl ., for instance, in Git BASH to open up a new Sublime Project in your current directory.
(MANDATORY):
Edit the .gitconfig file found in your home directory: C:UsersMY_USER_NAME.gitconfig, by adding the following to it. Notice the subtle changes from the Linux instructions above:
- Notice that you must specify the full path to the Sublime Text executable. Note the direction of the slashes! Use
/NOTto separate folders in the path name! (Thanks VonC for helping me see this). - Our
sublalias we made for Git BASH above doesn't work here, so you can't use it like we did in the Linux example, instead you must specify the whole path as shown above. - The
~symbol, however, does still work here to get to your Windows home directory.
2.5. (Optional) Install the 'Git' package into Sublime Text 3.
This gives you syntax highlighting for git commit messages, as well as access to other git commands such as git blame (which I use frequently in Sublime Text) or git commit (which I don't use in Sublime Text since I'd prefer the command-line for general git flow, as I've mentioned in my comments below this answer).
To install a package: First, ensure “Package Control” is installed. Next, press Ctrl + Shift + P (same as Tools → Command Palette) and type all or part of “Package Control: Install Package”, then press Enter. In the search box that comes up, search for the package 'Git' and hit Enter on it, or click on it, to automatically install it.
Once installed, Ctrl + Shift + P then searching for 'git' will bring up git commands you can use internally inside Sublime Text now, such as git blame.
3. Use it
Now when you call git commit, for instance, as normal from the command-line, Sublime Text will open up into the .gitconfig.sublime-project we created above, with that project's settings! As you type a paragraph you'll notice it extends past the ruler we set since soft word-wrap is off. To force hard wrap via auto-inserted hard-returns at the end of each line, put your cursor on the long line you want auto-wrapped and press Alt + Q. It will now hard-wrap/hard-fold at 72 chars, which is what we set in the project settings' 'rulers' parameter above.
Now, save your commit message with Ctrl + S, and exit (to complete your git commit) with Ctrl + Shift + W.
Done!
Gabriel StaplesGabriel StaplesMvim as your git editor
Like all the other GUI applications, you have to launch mvim with the wait flag.
For Windows users who want to use neovim with the Windows Subsystem for Linux:
git config core.editor 'C:/Windows/system32/bash.exe --login -c 'nvim .git/COMMIT_EDITMSG'
Text Editor For Mac
This is not a fool-proof solution as it doesn't handle interactive rebasing (for example). Improvements very welcome!
brcolowbrcolowJust try EDITOR=vim git commit.
Or you can set your EDITOR to vim by export EDITOR=vim in your bashrc.
For users of TextWrangler from the Mac app store:
Also, make sure your 'TextWrangler > Preferences > Application > When TextWrangler becomes active:' setting is set to 'Do nothing'
This works for me on OS X 10.11.4 with TextWrangler 5.0.2 from the Mac app store.
Explanation:
The -n means open in a new instance.
The -W means to wait until the application exits before using the contents of the edited file as the commit message.
The -a TextWrangler means use the TextWrangler application to open the file.
See man open in your Mac Terminal app for more details.
When using git-review I had to modify sequence.editor value to be able to do interactive rebase (git rebase -i -p):
gvim require: apt install vim-gtk
References
Édouard LopezÉdouard LopezThis opens Textmate editor in when you want to edit your commits.Requires textmate command line tools to be installed.
git config --global core.editor 'mate -w'
Git Editor Macvim
code ninjaFor Windows users who want to use Kinesics Text Editor
Create a file called 'k.sh', add the following text and place in your home directory (~):
At the git prompt type:
Mike CheelGit Editor For Windows
Mike CheelDownload Git For Mac
protected by Aniket ThakurJan 18 '18 at 9:01
Thank you for your interest in this question. Because it has attracted low-quality or spam answers that had to be removed, posting an answer now requires 10 reputation on this site (the association bonus does not count).
Would you like to answer one of these unanswered questions instead?